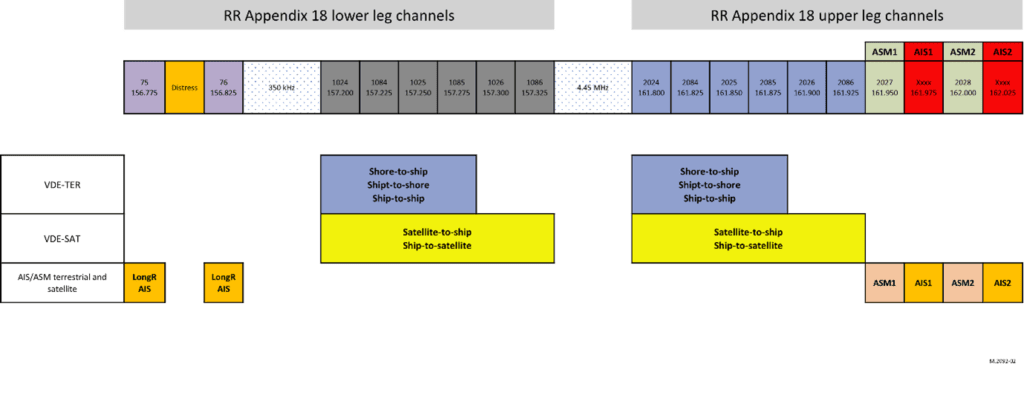
Sternula has more than 10 years of experience in developing and standardizing VDES technology. Our co-founder is the chairman of IALA E-Nav WG3, and we are the co-founder of the
VDES Alliance. Furthermore, Sternula is the first commercial satellite operator of AIS 2.0 (VDES).